Bronchitis
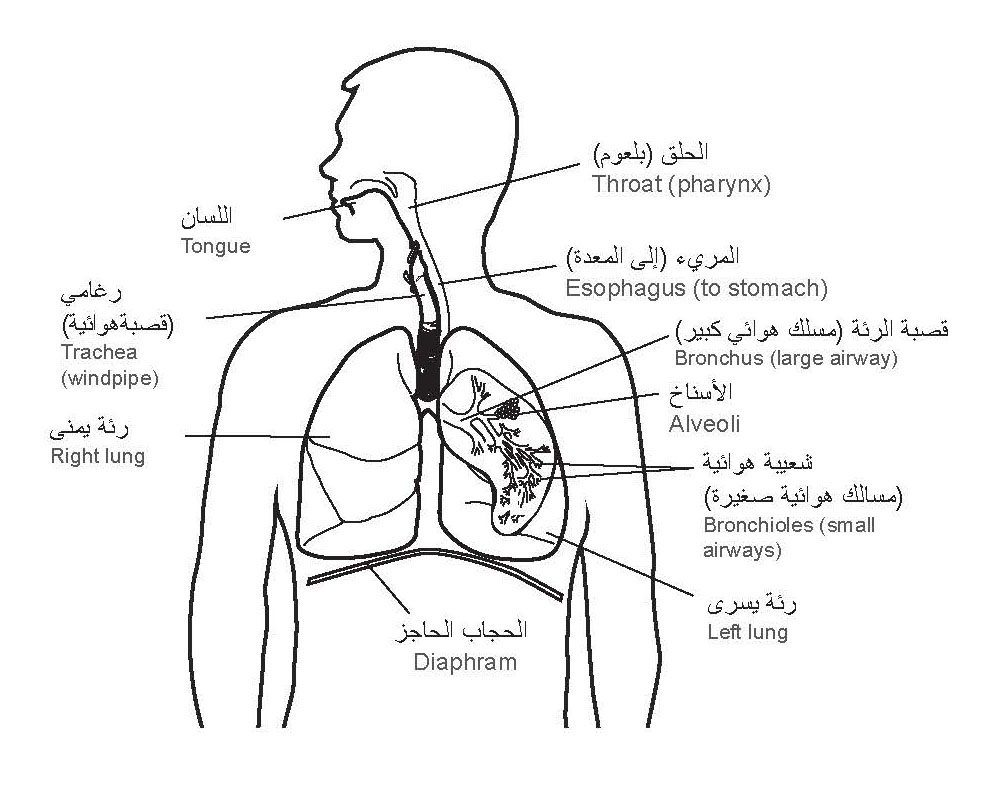
Bronchitis is swelling of the lining of the large airways called bronchi in the lungs. The
swelling causes more mucus than normal to be made. This can block the airflow through the lungs and may damage the lungs.
Acute bronchitis often starts to get better in days, but the cough may last 2 to 4
weeks. Over the counter medicines can help to control aches, fever and loosen
mucus. Treatment by your doctor may not be needed unless you are not feeling better or you have more trouble breathing.
Chronic bronchitis is a long-term disease of the lungs. It is one disease in a group
of lung diseases called COPD or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The damage
often gets worse over time and cannot be cured.
Signs of Bronchitis
- A frequent cough, often with yellow or green mucus.
- Feeling tired.
- Chest pain with coughing or deep breathing.
- Noisy breathing such as wheezing or whistling.
- Shortness of breath.
- Body aches.
- Fever or chills.
- Sore throat.
- Runny or stuffy nose.
Causes of Bronchitis
- Bacterial or viral infections.
- Smoking.
- Air pollution.
- Allergy to something in the air such as pollen.
- Lung disease such as asthma or emphysema.
Your Care
Your care may include medicines and breathing exercises to help you breathe
easier. You may need oxygen if you have chronic bronchitis. Your care may also
include:
- Avoiding colds and the flu.
- Wash your hands well and often to lower your risk of infections.
- Drinking a lot of liquids to keep mucus thin.
- Using a humidifier or vaporizer.
- Using postural drainage and percussion to loosen mucus from your lungs. You will
be taught how to do this. - Get a flu shot each year and talk to your doctor about getting the pneumonia
vaccine.
To Breathe Easier
- Quit smoking. The only way to slow the damage of chronic bronchitis is to quit
smoking. It is never too late to quit. - Do not drink alcohol. It dulls the urge to cough and sneeze to clear your air passages. It also causes your body to lose fluid, making the mucus in your lungs thicker and harder to cough up.
- Avoid things that irritate your lungs such as air pollution, dusts and gases.
- Sleep with your upper body raised. Use foam wedges or raise the head of your bed.
Call your doctor right away if you:
- Have chills or a fever over 101 degrees F or 38 degrees C.
- Need to use your inhalers or breathing treatments more often.
- Have more mucus, the color changes or it becomes too hard to cough up.
- Have a new or worsening gray or blue tint of your nails or the skin of your fingers or mouth.
- Have trouble talking or doing your normal activities.
- Have to use more pillows when sleeping or start having to sleep in a chair to breathe at night.
Call 911 right away if you:
- Cannot get your breath.
- Become confused, dizzy or feel faint.
- Have new chest pain or tightness.
Talk to your doctor or nurse if you have any questions or concerns.
To read more: Click here
© 2005 – February 14, 2021, Health Information Translations.
Unless otherwise stated, user may print or download information from www.healthinfotranslations.org for personal, non-commercial use only. The medical information found on this website should not be used in place of a consultation with your doctor or other health care provider. You should always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health care provider before you start or stop any treatment or with any questions you may have about a medical condition. The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Mount Carmel Health System, OhioHealth and Nationwide Children’s Hospital are not responsible for injuries or damages you may incur as a result of your stopping medical treatment or your failure to obtain treatment.
Bronchitis. Arabic.c